Sunrise
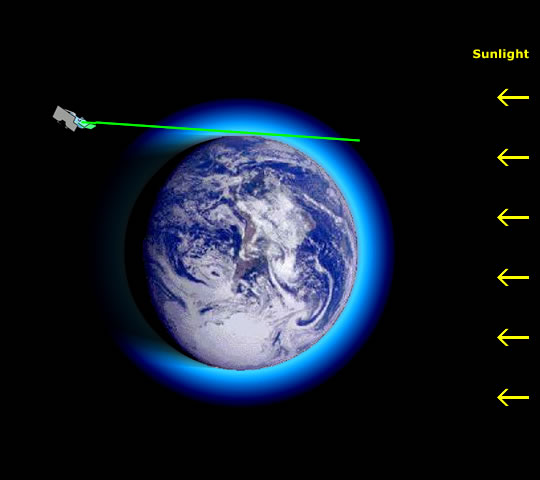
Fig 1.3.2.2.1.1: SCIAMACHY solar occultation.
Image courtesy of :
With every transit out of the nightside into the dayside zone SCIAMACHY sees the sun rise through the Earth's atmosphere. During this time the instrument performs a solar occultation.
The strong direct light source produces a good signal-to-noise ratio in the spectrometer, enabling the use of short integration times and providing a large number of measurement points compared with measurement of scattered light.
Measurements continue until the line of sight to the sun is outside the atmosphere, finally producing a reference solar spectrum that is used for autocalibration in retrieval algorithms.
Moonrise
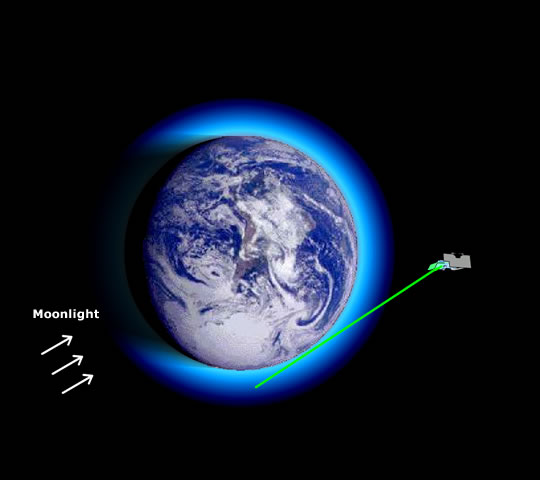
Fig 1.3.2.2.1.2: SCIAMACHY lunar occultation.
Image courtesy of :
The lunar occultation stage that takes place when SCIAMACHY passes from dayside into the nightside is similar in its procedure and results to the solar occultation.
Advantages and disadvantages of these measurement modes
- Solar occultation mode measurements provide the most sensitive and precise profile retrievals. Gas, temperature and pressure profiles can be retrieved from an altitude of 15 km up to 60 km.
- Lunar occultation mode measurements provide data on the night-time chemistry in the atmosphere.
- Solar and lunar occultation mode measurements can each be performed only once per orbit, resulting in a limited geographical coverage.
- Furthermore, lunar occultation mode measurements are even more infrequent, being only possible on the 5–8 days of the ~28 day lunar cycle on which SCIAMACHY experiences a moonrise.
- Because both solar and lunar occultation measurements can only be performed in the transition zones between dayside and nightside, solar occultation is restricted to latitudes between 65°N and 90°N and lunar occultation to latitudes between 30°S to 90°S.