Wavelength (λ, m)The wavelength of a wave is the distance between corresponding points on the wave separated by one period, e.g. the distance from peak to peak. Frequency (ν, Hz)The frequency of a wave is the number of waves passing a location per unit time. In a vacuum wavelength and frequency are related by where c is the speed of light, 2.99792458 x 108 (m·s–1) Wavenumber (
|
|
Radiant energy (Q, J)The energy carried by electromagnetic radiation. Radiant flux (P, W)Radiant energy transmitted in a radial direction per unit time. Monochromatic radiant flux (Pλ, W·m-1)Radiant energy transmitted in a radial direction per unit time per wavelength range. |
 |
Irradiance (E, W·m-2)Radiant flux incident upon a surface per unit area. Also known as total flux. Monochromatic irradiance (Eλ, W·m-2·m-1)Radiant flux incident upon a surface per unit area per wavelength range. |
 |
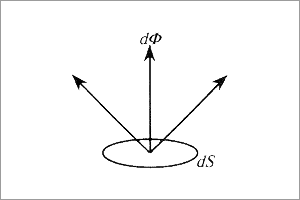
Radiant emittance (M, W·m-2)Radiant energy radiated from a unit area per unit time. |
 |
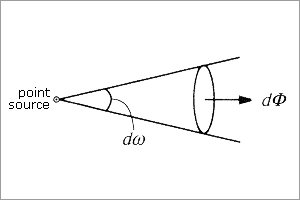
Radiant intensity (Φ, W·sr-1)Radiant flux radiated from a point source per unit solid angle in a radiant direction. |
 |
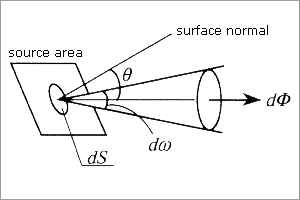
Radiance (I, W·m-2·sr-1)Radiant intensity per unit projected area in a radial direction. Monochromatic radiance (Iλ, W·m-2·m-1·sr-1)Radiant intensity per unit projected area in a radial direction per wavelength range. |
 |
steradian (Ω, sr)The steradian is an important unit for radiation calculations. It is
the 'solid angle' which, having its vertex at the centre of the sphere, cuts
off an area equal to the square of the radius of the sphere.
|