Snell's Law describes the refraction that takes place when light passes between media of different optical densities. When light crosses from one medium into an optically denser medium it is refracted towards the normal.
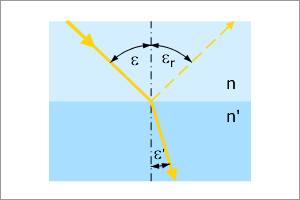
Fig 2.3.4.1: Snell's Law of refraction
Image: AT2-ELS
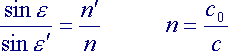
In the atmosphere, light is bent towards the normal when it passes from an optically thinner to an optically thicker layer.
Atmospheric refraction
- depends on wavelength (larger for shorter wavelengths);
- depends on density, and thus air humidity and temperature;
- is largest in the troposphere.
In practice, the atmosphere is subdivided into layers, and the ray refracted at the layer interfaces:
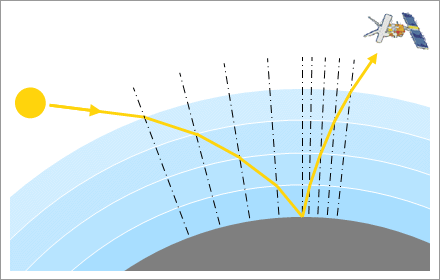
Fig 2.3.4.2: Refraction at the interfaces of atmospheric layers
Image: AT2-ELS
As a result of atmospheric refraction
- the sun appears higher in the sky than it is;
- the sun is flattened at sunrise and sunset;
- we have to distinguish between the astronomical and the local solar zenith angles.
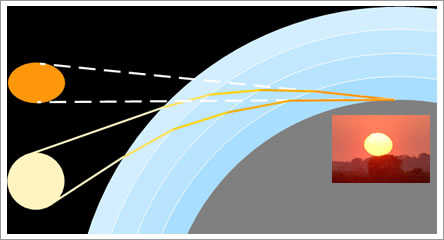
Fig 2.3.4.3: Refraction at sunset
Image: AT2-ELS
Refraction in combination with layering in the atmosphere also leads to other effects such as mirages and the 'green flash'.
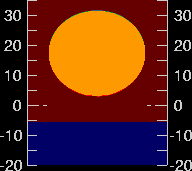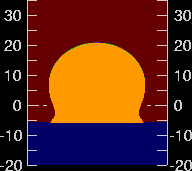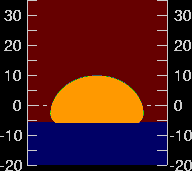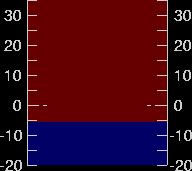
Fig 2.3.4.4: Animated simulation of refraction effects at sunset
Animation: San Diego State University, Department of Astronomy. See Green-flash simulations