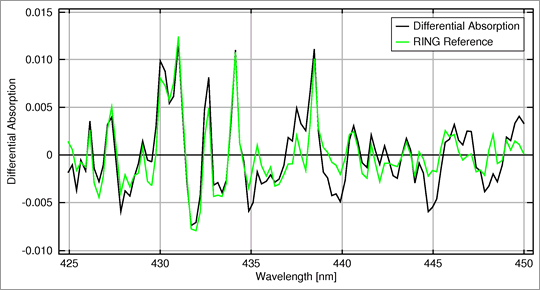
Fig 3.3.1.10.1: Differential absorption curve and Ring reference curve.
Image: AT2-ELS
In the DOAS procedure a pseudo absorption cross-section curve is first fitted to the differential absorption curve in order to correct for the Ring effect. This effect is produced by inelastic Raman scattering, which reduces the depth of the Fraunhofer lines in the scattered light of earthshine compared with unattenuated solar irradiation.
This effect — called the Ring effect after its discoverer James Ring — can produce anomalies of up to several percent in the UV spectral range, which, if uncorrected, would be enough to mask weak atmospheric absorptions.
A discussion of the Ring effect and a simulation of the generation of a Ring effect pseudo-absorber is given in the section on 'Earthshine interactions'.